
In the first instalment of our series on artificial intelligence (AI), we provided an overview of the technology’s disruptive potential, its history, and current – and rapidly evolving industry structure. In this instalment, we expand upon how AI already complements myriad industries and business functions. We also explore how the technology can benefit consumers and discuss why we believe investors must take a holistic approach when assessing how AI will impact the growth and earnings trajectory of individual companies.
An opportune time
A central reason for investor enthusiasm in AI can be found in economic and demographic reality. The two main drivers of gross domestic product (GDP) growth are expanding populations and rising productivity. The world is getting older and needs new growth levers. This is especially true for advanced countries with service-oriented economies. In the U.S., for example, population growth is expected to slow from 0.6% annually to 0.2% over the next three decades, and productively has remained mired below its long-term average since the Global Financial Crisis. The upshot is that the U.S. and global economy both need a catalyst to keep GDP growth – and national wealth – at a level sufficient to meet society’s obligations.
Enter AI. Similar to what automation has done for manufacturing over the past several decades, AI stands to boost productivity in the services sector. Rather than viewing AI-led disruption as a jobs killer – a narrative that accompanies many technological innovations – it’s more practical to see it as the type of productivity enhancer that creates more value-added positions. The higher salaries commanded by such roles are a fundamental input of growing an economy.
A broad canvas
Unlike other recent technological advancements, AI has the potential to impact every facet of an enterprise – from front office to back office and even product development. Its reach will be felt across industries and extend to government. Already AI is being deployed to improve the interface of historically challenging customer support functions. In the future, the expectation is for AI to leverage large data sets and specific customer information to rapidly assess any issues and present viable solutions. Such developments could represent a win-win for both the customer and the enterprise, potentially turning a worst-in-class touch point into a competitive advantage by rapidly anticipating and solving problems.
In addition to addressing customer retention, AI models can be aimed at growing revenues by seeking to identify new customers and expanding into new markets. Central to the existing internet search business model is algorithm-based advertising. AI, in our view, has the potential to turbocharge that. The ability of AI-models to more effectively segment and profile customers should lead to improvements in targeted and customized advertising. This, in turn, should increase conversion rates and lower acquisition costs.
AI in motion: Advertising

Source: Janus Henderson Investors.
Driving efficiencies
We believe middle- and back-office functions present considerable opportunity for AI to wring out efficiencies in organizations. Many of these functions are highly complex and errors can have material financial or regulatory impact. Other tasks are rote and could be executed more rapidly and effectively by a bot. Functions primed to be improved by AI include accounting, legal and compliance, and coding – a process especially important for companies heavily reliant on software.
While hidden from most employees and customers, the ubiquity of software designed to carry out a range of functions can greatly benefit organizations but also expose it to risks – a phenomena often on display in high-profile mishaps. AI can not only undertake more mundane aspects of writing code, but also test, assess, and debug issues considerably faster than humans, limiting the risks posed by errors and reducing associated costs.
Product discovery
Across industries, AI is being used to test and refine existing products as well as identify new ones. Perhaps no other industry, however, will feel AI’s impact more with respect to product discovery than healthcare.
Identifying new drug compounds and therapies to address specific diseases is notoriously complex. And discovery is only the first step in a highly regimented trial process that also involves testing for efficacy and safety. AI has the potential to make connections between diseases, underlying causes, and potential treatments far beyond the scope of what’s possible by highly skilled humans.
In addition to drug development and testing, AI can be used to customize and monitor treatment plans. These efficiencies should have material economic and societal impact by raising clinical trial success rates, reducing costs and time to market and, most importantly, improving patient outcomes.
An “assist” to the consumer
It is not just corporations and business functions that will benefit from AI’s efficiencies; consumers will also see many daily tasks streamlined.
The AI-enabled internet search functions that are increasing conversion rates for advertisers will also improve the experience of consumers when conducting searches, limiting the rabbit holes that often accompany the process. After a series of fits and starts, consumers are increasingly integrating voice assisted devices and functions into their daily routines, allowing for multi-tasking and answering quick queries. Voice devices are just one aspect of the wider adoption of productivity assistance that can combine a person’s schedule with larger data sets and optimize their “to do” list. We believe that this functionality will only increase as the data footprint of our lives continues to grow.
Initial consumer use cases for AI

Source: Janus Henderson Investors.
Investment implications: Not a slam dunk
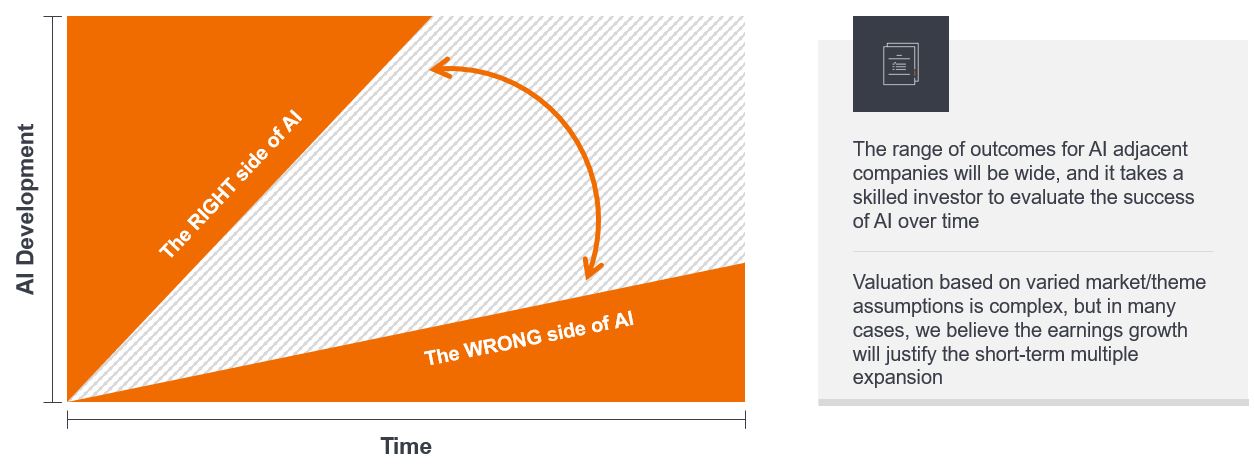
While the efficiencies reaped by AI will reverberate across the global economy, gaining optimal investment exposure to this powerful theme is not simple. Given the multiple ways businesses can leverage AI, the range of operational – and ultimately investment – outcomes for an individual organization has widened. Some companies will have highly effective AI strategies while others either execute poorly or misplace their priorities, diminishing the potential returns on what could be a hefty investment.
Wide range of outcomes for companies
We are not in early innings, we are just throwing the first pitch.
Source: Janus Henderson Investors.
In our earlier note, we spoke about the building blocks enabling the AI revolution. With respect to the companies that deploy AI, we believe organizations must be measured on an individual basis. Highlighting the potential for this theme, many AI strategies have direct oversight by a company’s CEO or immediate lieutenants. In coming years, these initiatives’ fruits will be measured in increased revenues, higher margins, better customer retention, and product innovation.
Although time will tell which companies got it right, in the meantime, investors face an environment where valuations can appear high for companies – accurately or otherwise – associated with the AI theme. While we believe the potential for attractive compounded earnings growth justifies many of these valuations, other companies will get it wrong and wind up on the wrong side of the AI divide.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Health care industries are subject to government regulation and reimbursement rates, as well as government approval of products and services, which could have a significant effect on price and availability, and can be significantly affected by rapid obsolescence and patent expirations.
Technology industries can be significantly affected by obsolescence of existing technology, short product cycles, falling prices and profits, competition from new market entrants, and general economic conditions. A concentrated investment in a single industry could be more volatile than the performance of less concentrated investments and the market as a whole.
These are the views of the author at the time of publication and may differ from the views of other individuals/teams at Janus Henderson Investors. References made to individual securities do not constitute a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any security, investment strategy or market sector, and should not be assumed to be profitable. Janus Henderson Investors, its affiliated advisor, or its employees, may have a position in the securities mentioned.
Past performance does not predict future returns. The value of an investment and the income from it can fall as well as rise and you may not get back the amount originally invested.
The information in this article does not qualify as an investment recommendation.
There is no guarantee that past trends will continue, or forecasts will be realised.
Marketing Communication.