
Bond markets are confounding the consensus view that they would exhibit the same aggressive repricing to higher yields seen in 2016 on a Trump election victory.
Figure 1: Change in 10-year government bond yields one week after the US election (Nov 2016 and Nov 2024)

Source: Bloomberg, US 10-year government bond yield. Germany 10-year government bond yield, UK 10-year government bond yield. 8 November 2016 to 15 November 2016, 5 November 2024 to 12 November 2024. Basis point (bp) equals 1/100 of a percentage point, 1bp = 0.01%. Yields may vary over time and are not guaranteed.
To some extent this assumption seemed to be based on a muscle memory of 2016 and a generalised view that Trump = unbridled fiscal expansion. However, even as it appears likely we see a Republican sweep, the US yield curve has flattened and US bond yields are little changed from pre-election levels.
Meanwhile, in other countries, bond yields have fallen as the growth risks of Trump’s tariff plans remain considerable, with arguably little inflationary impact. An interesting case study that we highlighted in October, of the potential effects on inflation and growth, is shown below.
Figure 2: Estimated impact of Trump tariffs on US and Euro Area
Much heavier burden on European growth offers net dovish impulse for the European Central Bank
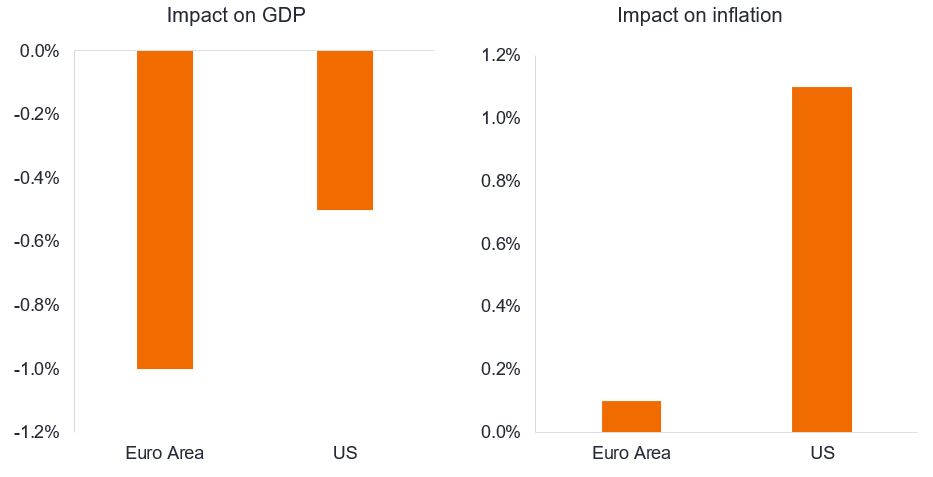
Source: Goldman Sachs, Jans Hatzuis, “Implications of Higher Tariffs for Euro Area and US Monetary Policy”, at the European Central Bank Forum, 2 July 2024. Assumes 10% tariffs across the board and full retaliation. There is no guarantee that past trends will continue, or forecasts will be realised. The views are subject to change without notice.
The price action in the immediate aftermath of the election results has been logical in our view reflecting:
- Tariff risks discussed above.
- A bond market that is already pricing in only three more interest rate cuts in the US to a level that would likely still be above a neutral rate for the US economy. With US mortgage rates around 7%1 again, this market pricing is not one in which we necessarily expect to see a steepening yield curve.
- An energy policy aiming to increase supply and keep the price of oil capped.
Against this, on the fiscal front the market fully expects a renewal of the Trump 2017 tax cuts, which were due to expire in 2025. However, this is not fiscal stimulus for economic growth per se, it simply prevents unforeseen tax hikes. On the spending side there may well be offsets as the new administration seeks efficiencies, whilst the ability of tariffs to raise government revenue also remains important to consider. The outlook for growth stimulating fiscal spending therefore remains somewhat murky.
In October, we expressed the view that a Trump sweep would not see a replay of the painful bear steepening witnessed eight years ago and that a Trump win could potentially act as a positive catalyst for German bond prices leaving US bonds a relative underperformer.
Germany’s exporting economy is facing multiple headwinds: weakness in China weighing on German exports, competition from China in electric vehicles, and now the threat of tariffs on its exports to the US. This is already affecting domestic politics, with Germany set to hold snap elections in February. With Germany and France in something of a political vacuum, the European Commission will have its work cut out negotiating with the new US administration.
For Trump we are told that ‘personnel is policy’. On that score, we await news of the appointment of the Treasury Secretary as regards fiscal policy, while the possible return of Robert Lighthizer – well known for his protectionist and tough negotiating views – as US Trade representative in the new administration offers further indications of tariff policy. In the meantime, for non-US investors, Lighthizer’s book “No Trade is Free”, published in 2023, gives a precis of the risks to individual countries from a Trump 2.0 trade policy.
1Source: Bloomberg, Bankrate.com US home mortgage 30-year fixed national average, 11 November 2024.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Fixed income securities are subject to interest rate, inflation, credit and default risk. The bond market is volatile. As interest rates rise, bond prices usually fall, and vice versa. The return of principal is not guaranteed, and prices may decline if an issuer fails to make timely payments or its credit strength weakens.
Bear steepening: A situation where yields on longer-term bonds rise more than the rise in yield on shorter-term bonds.
Neutral rate: An interest rate at which the economy operates at full employment and with stable inflation, i.e. a rate that is neither expansionary or contractionary for the economy.
Yield curve: A graph that plots the yields of similar quality bonds against their maturities. In a normal/upward sloping yield curve, longer maturity bond yields are higher than short-term bond yields. With an inverted yield curve, yields are higher on shorter-dated bonds than longer-dated bonds. A yield curve can signal market expectations about a country’s economic direction.