
A steep credit curve emerges
2024 has been a scorching year for European CLO issuance, with around EUR€41 billion of gross new supply issued so far1 and it looks likely to be a post-GFC calendar year record for new CLO creation. Balanced with strong investor demand, this has seen CLO spreads move sideways in recent months, largely on this dynamic. However, a deeper dive into the valuations shows some pricing dislocations.
At first glance, spreads for the AAA-rated senior tranches appear tight at current levels, with secondary market spreads for mid-tenor2 AAA-rated CLO at around 100bps3 and certain short-dated securities trading inside of 80bps. By contrast, longer-dated new issue AAA CLO is typically pricing nearer to 130bps for top-tier CLO managers4. This steep term premium5 is a relatively uncommon phenomenon, with the CLO credit curve generally quite flat in benign market conditions. As shown in Figure 1, a sample of recent AAA CLO bids and offers6 evidence a pronounced upward slope to the curve – ie. long-term bonds are pricing with (unusually) wide spreads relative to short-term bonds.
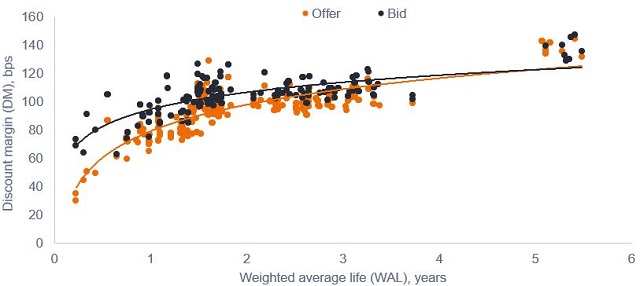 Source: Bloomberg, Janus Henderson, 21 October 2024. Based on a sample of live bids and offers on this date for European AAA-rated CLOs. Curves are logarithmic based on this sample. Discount margin (DM) is the average expected return of a floating-rate security (typically a bond) that’s earned in addition to the index underlying, or reference rate of, the security.
Source: Bloomberg, Janus Henderson, 21 October 2024. Based on a sample of live bids and offers on this date for European AAA-rated CLOs. Curves are logarithmic based on this sample. Discount margin (DM) is the average expected return of a floating-rate security (typically a bond) that’s earned in addition to the index underlying, or reference rate of, the security.Supply dynamics distort spreads
To put some numbers to this, a AAA CLO spread of 85bps is screening exceptionally tight at around the 10th percentile relative to its range over the last 10 years, whereas 130bps4 for newly issued securities is just above the median average. All of this begs the question as to what is driving this yawning term premium: in short, the elevated supply of new issue CLOs has been generally issued with longer tenors, keeping those longer-dated spreads wider. Meanwhile, more risk averse investors have been happy to continue to pick up shorter-dated bonds, confident they will receive both their sliver of spread and principal back in the near term.
Given the relatively benign environment, with low corporate defaults, we think the long end of the CLO credit curve constitutes good value and could warrant taking on the additional spread duration7 for what are very high-quality bonds.
Looking down the capital stack, new issue AA CLOs are also pricing around historic 10-year median spread levels, at 200bps in the primary market. Simultaneously, short-dated A CLOs, a grade lower, are trading at similar levels in the secondary market. This is shown in Figure 2, which shows where spreads currently sit, relative to the past 10 years, with AA CLOs clearly trading cheaper.
Figure 2: AA and A CLO credit spread ranges – percentile rank vs history
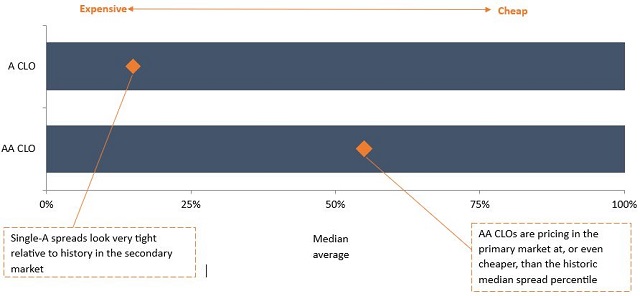
Source: JP Morgan, Janus Henderson calculations, 31 October 2024. Based on a 10-year lookback of European AA and A-rated CLO spread levels.
Assessing relative value
From a relative value perspective then, A rated CLOs look very expensive compared to AAs. Indeed, the ability to buy AA rated bonds in the primary market near the same spread levels and cash price as A bonds in the secondary market (albeit for shorter profiles), we believe highlights some distortion in market pricing. Anecdotally, we are hearing there is significant demand from select North American investors for European A CLOs, which has driven its spreads materially tighter and compressed the spread basis between those two tranches.
While neither rotating into new issue AAA CLOs nor exchanging secondary A-rated bonds for AA in primary markets offer a ‘free lunch’, we think both fundamentals and the supply/demand dynamics remain supportive. Investors who can stomach the added spread duration risk could be well compensated.
Footnotes
1 Source: Morgan Stanley, 5 November 2024.
2 Around three years.
3 Source: JP Morgan, Janus Henderson, based on observed transactions, 31 October 2024.
4 Source: Janus Henderson based on observed supply, 31 October 2024.
5 The term premium is the additional credit spread, or compensation, received for buying longer bonds overshorter dated bonds.
6 The bid is the highest price an investor is willing to pay for a security. The offer is the lowest the seller (or issuer) is willing to sell the security for.
7 Spread duration is the sensitivity of a bond’s price to a move in its own credit spread. A “higher” spread duration means that the price of a bond is more sensitive to a move in credit spreads.