
Following the sharp reset in interest rates over the past year, investors are looking afresh at bonds given the higher yields on offer today from the asset class. In fact, yields on global investment grade corporate bonds are hovering around the highest they have been since 2009 (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Yield on global investment grade corporate bonds
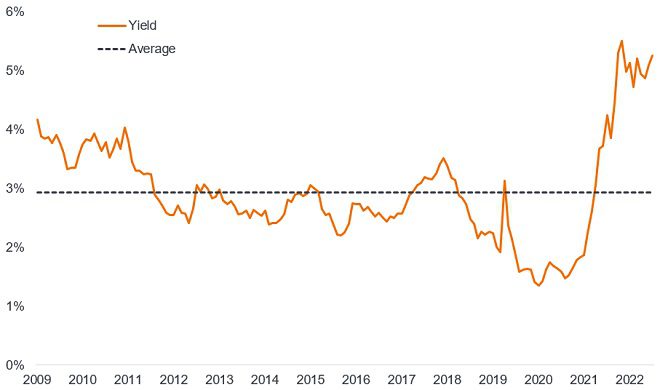
Source: Bloomberg, ICE BofA Global Corporate Index, yield to worst, 31 December 2009 to 30 June 2023. The ICE BofA Global Corporate Index tracks investment grade corporate debt publicly issued in the major domestic and Eurobond markets. Yield to worst (YTW) is the lowest yield a bond can achieve provided the issuer does not default and accounts for any applicable call feature (i.e. the issuer can call the bond back at a date specified in advance). Yields may vary over time and are not guaranteed.
Rewind the clock back and for much of the past decade an investor would have had to do at least one of the following three actions to achieve a yield above 5%:
- Take on more duration risk (interest rate sensitivity) by investing in bonds with long maturities.
- Accept lower credit quality by investing in sub-investment grade bonds and therefore be more exposed to bonds that might potentially default.
- Take on emerging market risk by investing in bonds from outside developed markets.
That is not to say those would have been bad decisions – in fact, each of those actions would have offered opportunities as well as risks. What stands out today, however, is an opportunity to capture a high level of income for relatively low risk. A yield of 5% or more may be achieved by investing in predominantly investment grade bonds.
What is particularly exciting about today’s bond market is that the front end of the yield curve is offering historically high yields. Today, investors can capture most of the yield available within global corporate bonds without having to stretch to long maturities; practically all the yield can be achieved with shorter dated bonds (1-5 years) as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Yield differential
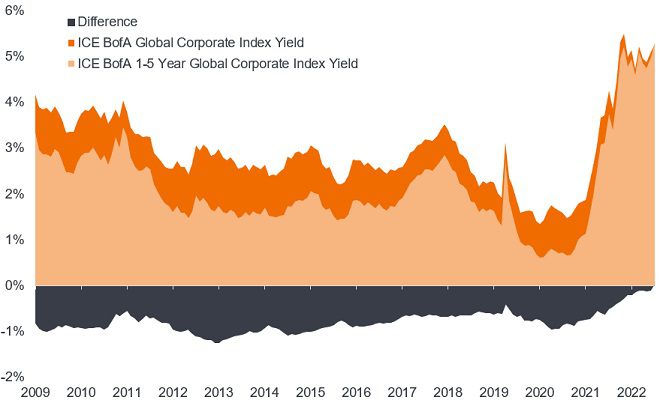
Source: Bloomberg, ICE BofA Global Corporate Index, ICE BofA 1-5 Year Global Corporate Index, yield to worst, 31 December 2009 to 30 June 2023. Definitions for yield to worst as per source in Figure 1. The ICE BofA 1-5 year Global Corporate Index is a subset of ICE BofA Global Corporate Index including all securities with a remaining term to final maturity less than 5 years. Yields may vary over time and are not guaranteed.
A change in direction?
But these attractive yields at the shorter end may not be around for long. Central banks have been on a mission to drive down inflation by raising interest rates and they are beginning to see some success with headline consumer price index (CPI) inflation dropping in the past year from 9.1% in the US to 3.0% today and in the eurozone from 10.6% to 5.5% today.1 Interest rate futures markets are suggesting that we are approaching the peak in the US rate hiking cycle and that cuts could start within the next 12 months, particularly if the economy slows.2 Rising rate environments typically result in a cooling economy and subsequent rate cuts to boost economic activity. There is a risk, however, that the markets might be wrong and interest rates and bond yields might rise from here.
Short-term government bond yields are heavily influenced by central bank policy rates so yields on these bonds are likely to fall if interest rates and inflation head lower. In fact, the market tends to move in advance of policy decisions. Corporate bonds typically offer a credit spread (additional yield over a government bond of the same maturity) to help compensate for potential credit risk. If the economy weakens this could send credit spreads wider but yields on investment grade corporate bonds tend to have a strong relationship with directional moves in government bonds. If yields on government bonds start to decline in the coming year, higher quality corporate bond yields could head lower as well.
Investors could seek to lock in today’s yield by buying an individual bond, but we think that a fixed maturity bond fund would be a less risky route. Just like an individual bond it has a regular coupon and fixed maturity date but comes with the added benefit of diversification across a portfolio of bonds. Furthermore, credit selection is undertaken by a team of experts, who will monitor the portfolio throughout its fixed term, helping to avoid default risk and maximise the yield.
Taken together, investors have, in our view, a window of opportunity to lock in a historically high yield. And a fixed maturity bond fund offers a straightforward investment vehicle to achieve this.
1Source: Bloomberg, US Consumer Price Index, all items, urban consumer, year-on-year change to 30 June 2023. Eurozone harmonised index of consumer prices, year-on-year change to 30 June 2023. Correct as at 12 July 2023.
2Source: Bloomberg, US interest rate projections. Correct as at 14 July 2023. There is no guaranteed that past trends will continue or forecasts will be realised.
Corporate bonds: A debt security issued by a company. Bonds offer a return to investors in the form of periodic payments and the eventual return of the original money invested at issue on the maturity date.
Default: The failure of a debtor (such as a bond issuer) to pay interest or to return an original amount loaned when due.
High yield: A bond that has a lower credit rating than an investment grade bond. Sometimes known as a sub-investment grade bond. These bonds carry a higher risk of the issuer defaulting on their payments, so they are typically issued with a higher coupon to compensate for the additional risk.
Investment grade: A bond typically issued by governments or companies perceived to have a relatively low risk of defaulting on their payments. The higher quality of these bonds is reflected in their higher credit ratings.
Yield: The level of income on a security, typically expressed as a percentage rate. For a bond, at its most simple, this is calculated as the annual coupon payment divided by the current bond price.
These are the views of the author at the time of publication and may differ from the views of other individuals/teams at Janus Henderson Investors. References made to individual securities do not constitute a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any security, investment strategy or market sector, and should not be assumed to be profitable. Janus Henderson Investors, its affiliated advisor, or its employees, may have a position in the securities mentioned.
Past performance does not predict future returns. The value of an investment and the income from it can fall as well as rise and you may not get back the amount originally invested.
The information in this article does not qualify as an investment recommendation.
There is no guarantee that past trends will continue, or forecasts will be realised.
Marketing Communication.
Important information
Please read the following important information regarding funds related to this article.
- An issuer of a bond (or money market instrument) may become unable or unwilling to pay interest or repay capital to the Fund. If this happens or the market perceives this may happen, the value of the bond will fall.
- When interest rates rise (or fall), the prices of different securities will be affected differently. In particular, bond values generally fall when interest rates rise (or are expected to rise). This risk is typically greater the longer the maturity of a bond investment.
- The Fund invests in high yield (non-investment grade) bonds and while these generally offer higher rates of interest than investment grade bonds, they are more speculative and more sensitive to adverse changes in market conditions.
- Some bonds (callable bonds) allow their issuers the right to repay capital early or to extend the maturity. Issuers may exercise these rights when favourable to them and as a result the value of the Fund may be impacted.
- Emerging markets expose the Fund to higher volatility and greater risk of loss than developed markets; they are susceptible to adverse political and economic events, and may be less well regulated with less robust custody and settlement procedures.
- If a Fund has a high exposure to a particular country or geographical region it carries a higher level of risk than a Fund which is more broadly diversified.
- The Fund may use derivatives to help achieve its investment objective. This can result in leverage (higher levels of debt), which can magnify an investment outcome. Gains or losses to the Fund may therefore be greater than the cost of the derivative. Derivatives also introduce other risks, in particular, that a derivative counterparty may not meet its contractual obligations.
- If the Fund holds assets in currencies other than the base currency of the Fund, or you invest in a share/unit class of a different currency to the Fund (unless hedged, i.e. mitigated by taking an offsetting position in a related security), the value of your investment may be impacted by changes in exchange rates.
- When the Fund, or a share/unit class, seeks to mitigate exchange rate movements of a currency relative to the base currency (hedge), the hedging strategy itself may positively or negatively impact the value of the Fund due to differences in short-term interest rates between the currencies.
- Securities within the Fund could become hard to value or to sell at a desired time and price, especially in extreme market conditions when asset prices may be falling, increasing the risk of investment losses.
- Some or all of the ongoing charges may be taken from capital, which may erode capital or reduce potential for capital growth.
- The Fund could lose money if a counterparty with which the Fund trades becomes unwilling or unable to meet its obligations, or as a result of failure or delay in operational processes or the failure of a third party provider.
- In addition to income, this share class may distribute realised and unrealised capital gains and original capital invested. Fees, charges and expenses are also deducted from capital. Both factors may result in capital erosion and reduced potential for capital growth. Investors should also note that distributions of this nature may be treated (and taxable) as income depending on local tax legislation.