Subscribe
Sign up for timely perspectives delivered to your inbox.
The shape of modern portfolios are changing in a higher interest rate environment. In this 2024 outlook, David Elms, Head of Diversified Alternatives, explains why investors might consider giving alternatives a greater role in their portfolios as they plan for the future.

COVID, geopolitical tensions, and the end of the zero interest-rate policy era have marked the end of a decade-long run in both equity and bond markets. They have also raised questions around traditional approaches to constructing risk-adjusted, return-seeking portfolios.
So why is that? The negative correlation between equities and bonds has been a norm for investors since the 1990s. For most of this century, the traditional relationship between equities and bonds has been that when equities go up, bonds go down, and vice versa. This negative correlation has meant that a traditional portfolio, with nothing but equities and bonds, has naturally diversified itself.
However, the reverse has also been true for prolonged periods, notably the inflationary periods of the 1970s and ’80s. Indeed, if you look back over the decades prior to the noughties (Figure 1), equities and bonds have typically moved in the same direction. So if we are moving back into that higher interest rate environment, and there is some evidence that we are, then you need something else in your portfolio to properly diversify.
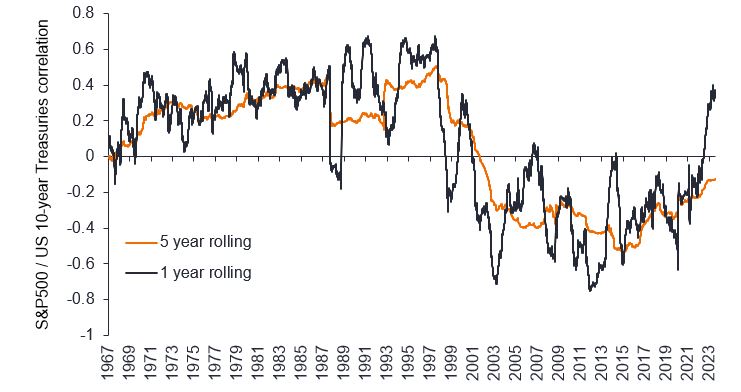
Source: Janus Henderson Investors, Bloomberg, as at 18 September 2023. Note: Data shows rolling correlation of the S&P500 vs US 10-year interest rate swap, using daily total returns. Data has been inverted to approximate S&P500 vs US 10-Year Treasury price, as opposed to US 10-Year Treasury yield. Past performance does not predict future returns.
Exogenous events, such as the US banking crisis, war in Ukraine and the Middle East, have also demonstrated that the negative correlation that investors have come to rely on, cannot be relied on in times of stress – when investors need diversification the most.
In such an environment of higher interest rates and rising geopolitical risk investors need to look elsewhere for diversification. This is where alternatives can offer something different. Diversification through strategies focused on absolute returns that are uncorrelated to both stocks and bonds. Putting that into a portfolio can help to compensate for the risk that equities and bonds may not move counter-cyclically to each other.
In order to be additive, we believe an alternatives strategy needs to provide investors with exposure to economically intuitive, statistically independent investment opportunities that adapt to the prevailing market environment. These abound across asset classes, warranting the need for a multi-faceted, multi-asset, multi-strategy approach. This includes opportunities that can be harnessed from higher interest rates, which can create better alpha opportunities for alternatives investors, given that the opportunity set can potentially improve by more than the increase in interest rates alone.
We see this in the world of mergers and acquisitions (M&A), where better deal spread premiums (Figure 2) offer the potential for higher returns, both in absolute terms and relative to cash. Merger arbitrage, effectively a bet that deals to merge companies will be completed, works better when the insurance premium for making that bet is higher, which can be reflective of the prevailing market environment, or other factors. We have seen a more interventionist regulatory regime in the US, for example, under President Biden. The US Department of Justice (DOJ) has been taking much greater interest in mergers to ensure they have a consumer benefit, or to avoid creating monopolies. This has added to the perception that more deals might be blocked, which creates risk and the potential for delay, which, in turn, ensures a higher insurance premium.
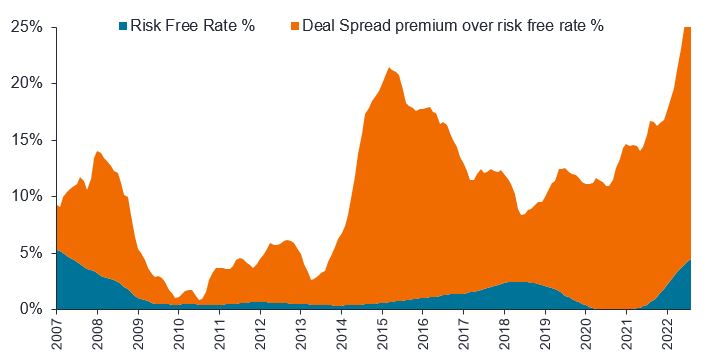
Source: Barclays, Bloomberg Global announced deals, Janus Henderson Investors Analysis, 30 November 2007 to 30 June 2023. Risk free rate used is SOFR 4months.
Mergers and acquisitions are an example of the broader phenomenon of better opportunities that are available during periods of higher interest rates, with the potential to drive higher excess returns in the future, as they have done in the past (Figure 3).
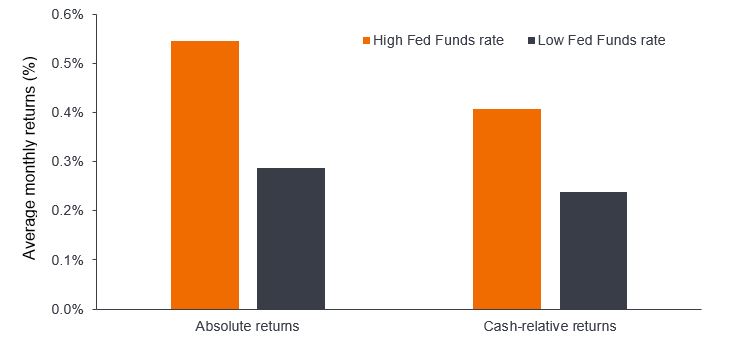
Source: InvestHedge Global Multi-Strategy USD Index (an index that measures the performance of Hedge Fund of Funds that combine a variety of strategies, used here to illustrate the global multi-strategy universe), average monthly returns, from 31 December 1997 to 31 August 2023. ‘High Fed Fund Rate’ defined as US Federal Funds Effective Rate >2%. ‘Low Fed Fund Rate’ defined as US Federal Funds Effective Rate <2%. Cash-relative returns deduct average Fed Funds rate from returns during each period. Past performance does not predict future returns.
At the same time, the uncertain economic and geopolitical outlook, plus stressed finances at a government, corporate and consumer level due to higher interest rates, are potential triggers for acute market stress in 2024. During these periods, seemingly unrelated strategies can become highly correlated. It is therefore also important to consider a strategy that seeks to provide a level of mitigation (or protection) during these stress events. Consideration for these defensively minded strategies has the benefit of allowing investors to remain exposed to positive long-term opportunities during difficult periods.
The ongoing shift from quantitative easing (QE) to quantitative tightening (QT) represents a potential challenge, both for alternatives and other asset classes. It is the transition from a QE environment to a QT environment that is difficult, because as spreads widen, it creates the potential for capital loss. We believe that we are most of the way through that widening process, but once the process is complete, we are much more comfortable with the longer-term outlook. But as highlighted earlier, there are ways that alternatives can help to mitigate that intervening period of uncertainty.
It is worth keeping in mind that there is an art as well as a science to investing. By nature, I tend to take a more quantitative view of investments, but a key benefit that has come from years of working in the financial industry is recognising that investing is ultimately a social science. It is the balance of supply and demand – human factors – that sets the price. And you need to factor that in more and more over time, to better understand what the maths can tell you. A different, and potentially difficult, backdrop for investors brings with it the need to think in new ways. In these transition periods, alternatives as an asset class has the potential to fulfil that need, aiming to deliver long-term positive returns that are not tied to equity markets or bonds, particularly on the downside.
Liquid alternative strategies are well placed to benefit from market volatility and a higher interest rate environment
Absolute returns: The total return of a portfolio over a specified period, as opposed to its relative return against a benchmark. It is measured as a gain or loss and stated as a percentage of a portfolio’s total value.
Alpha: The difference between a portfolio’s return and its benchmark index, after adjusting for the level of risk taken.
Correlation: How far the price movements of two variables (eg. equity or fund returns) move in relation to each other.
Counter-cyclical: Moving in the direction opposite to that of another asset, or the overall economy, effectively helping to dampen any fluctuations or volatility in performance.
Deal spread: The difference in value between the stock price of a target company and the offer or agreed price from an acquirer, which can often represent a significant premium to make the offer attractive to shareholders.
Diversification: A way of spreading risk by mixing different types of assets/asset classes in a portfolio, on the assumption that these assets will behave differently in any given scenario. Assets with low correlation should provide the most diversification.
Inflation: The rate at which the prices of goods and services are rising in an economy. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Retail Price Index (RPI) are two common measures.
Merger arbitrage: An investment strategy that aims to generate profits from successfully completed mergers and/or takeovers.
Quantitative easing (QE): An unconventional monetary policy used by central banks to stimulate the economy by boosting the amount of overall money in the banking system.
Quantitative Tightening (QT): A government monetary policy occasionally used to decrease the money supply by either selling government securities or letting them mature and removing them from its cash balances.
Risk-adjusted: A calculation of an investment’s return, or potential return, that takes into account the amount of risk required to achieve it.
Risk-free rate: The rate of return of an investment with, theoretically, zero risk. The benchmark for the risk-free rate varies between countries. In the US, for example, the yield on a three-month US Treasury bill (a short-term money market instrument) is often used.
Volatility: The rate and extent at which the price of a portfolio, security or index, moves up and down. If the price swings up and down with large movements, it has high volatility. If the price moves more slowly and to a lesser extent, it has lower volatility. The higher the volatility the higher the risk of the investment.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Volatility measures risk using the dispersion of returns for a given investment.
10-Year Treasury Yield is the interest rate on U.S. Treasury bonds that will mature 10 years from the date of purchase.
The S&P 500® Index reflects U.S. large-cap equity performance and represents broad U.S. equity market performance.
Alpha compares risk-adjusted performance relative to an index. Positive alpha means outperformance on a risk-adjusted basis.