JH Explorer in Sweden: Sunrise on green steel
Portfolio manager Tal Lomnitzer shares his excitement having seen how green steel is produced on a recent trip to the HYBRIT project in Sweden.
3 minute read
Key takeaways:
- The global steel industry produces around 7% of global CO2 emissions due to the blast furnace coking coal approach.
- Green steel can be made using hydrogen instead of coking coal as a reducing agent, producing H2O as the by-product instead of CO2.
| The JH Explorer series follows our investment teams across the globe and shares their on-the-ground research at a country and company level. |
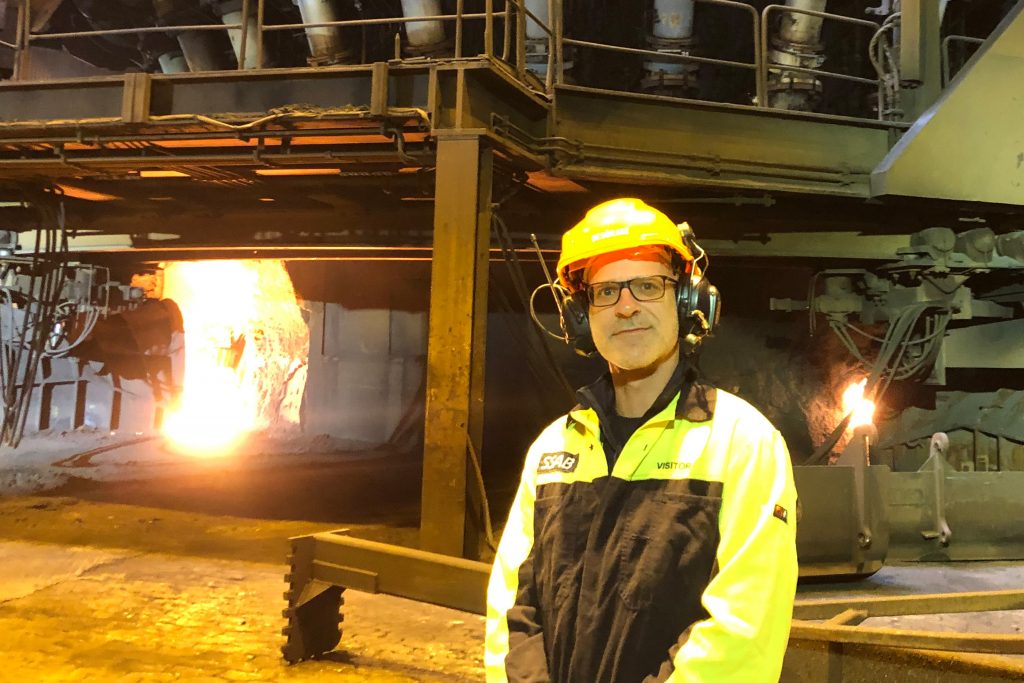
Luleå in far Northern Sweden is worth visiting as a tourist for the ‘midnight sun’ in the peak of summer when the sun does not set – instead one gets hours of sunset when it would normally be dark. My visit was purely work related to see a different kind of sunset – that of the way steel is currently produced.  The objective of my visit was to see the production of truly green, carbon-free steel at the HYBRIT pilot project, a joint venture between Swedish steel manufacturer SSAB, renewable power producer Vattenfall and high-quality iron ore producer LKAB. The HYBRIT technology used could potentially reduce Sweden’s total CO2 emissions by at least 10%, but more importantly could lead to a reduction in emissions from iron and steel production globally.*
The objective of my visit was to see the production of truly green, carbon-free steel at the HYBRIT pilot project, a joint venture between Swedish steel manufacturer SSAB, renewable power producer Vattenfall and high-quality iron ore producer LKAB. The HYBRIT technology used could potentially reduce Sweden’s total CO2 emissions by at least 10%, but more importantly could lead to a reduction in emissions from iron and steel production globally.*
At SSAB’s Luleå steel manufacturing plant they take high-grade iron ore pellets, heat it with coking coal to remove the oxygen, leaving pure molten iron and carbon dioxide. The blast furnace coking coal approach means that the global steel industry produces around 7% of global CO2 emissions**. This is why I was so excited to visit a project that uses hydrogen instead of coking coal, as a reducing agent.
The same molten iron is produced but instead of CO2, H2O is the by-product. This is truly ‘green steel’, assuming that the hydrogen used is green hydrogen made with renewable electricity. I was amazed to find out that in Northern Sweden there is capacity for about 20 terawatt hours of excess renewable electricity to make hydrogen to feed this process. That power could make a lot of green hydrogen. Good thing too because humanity is going to need a lot of steel to build wind farms, solar farms, and grid infrastructure to power a decarbonised, electrified future. We have the means, and I have now seen how steel can be made in a way that has a minimal environmental footprint.
This is so exciting – I feel like I have peered into the future to see the sun rise on a new dawn for the steel industry.
Goodbye blast furnaces – here is the old blast furnace that will be replaced with an electric arc furnace to melt briquettes using renewable power.

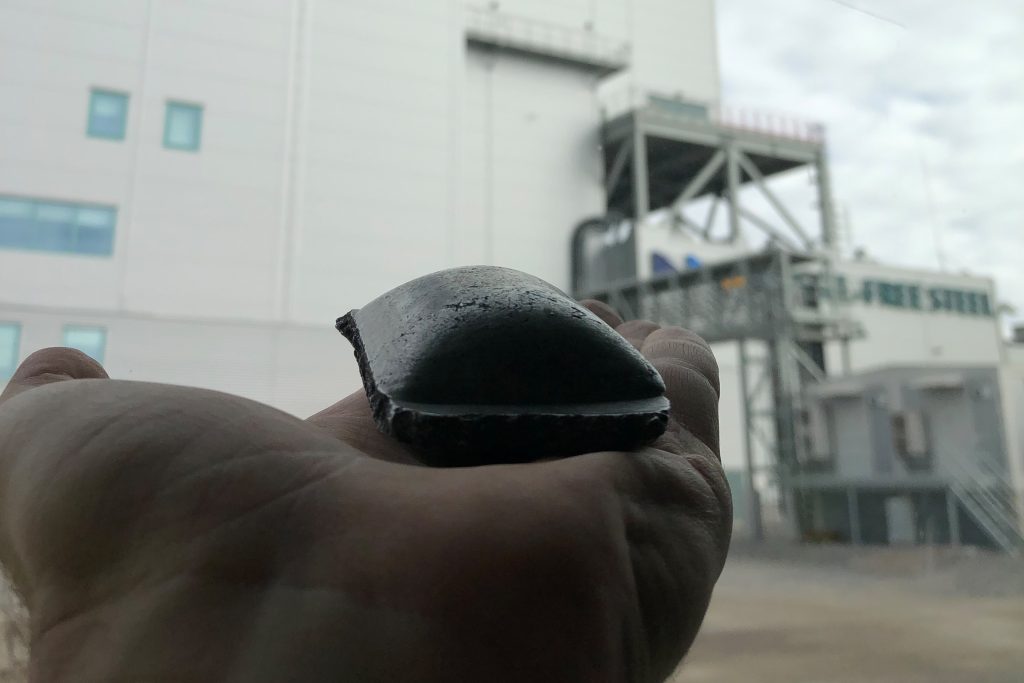
A fossil-fuel free briquette of pure iron in the palm of my hand.

Photos courtesy of Tal Lomnitzer, used with permission.
*https://www.hybritdevelopment.se/en
**UN Emissions Gap Report 2020.
JHI
These are the views of the author at the time of publication and may differ from the views of other individuals/teams at Janus Henderson Investors. References made to individual securities do not constitute a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any security, investment strategy or market sector, and should not be assumed to be profitable. Janus Henderson Investors, its affiliated advisor, or its employees, may have a position in the securities mentioned.
Past performance does not predict future returns. The value of an investment and the income from it can fall as well as rise and you may not get back the amount originally invested.
The information in this article does not qualify as an investment recommendation.
There is no guarantee that past trends will continue, or forecasts will be realised.
Marketing Communication.
Important information
Please read the following important information regarding funds related to this article.
- Shares/Units can lose value rapidly, and typically involve higher risks than bonds or money market instruments. The value of your investment may fall as a result.
- Shares of small and mid-size companies can be more volatile than shares of larger companies, and at times it may be difficult to value or to sell shares at desired times and prices, increasing the risk of losses.
- The Fund is focused towards particular industries or investment themes and may be heavily impacted by factors such as changes in government regulation, increased price competition, technological advancements and other adverse events.
- The Fund follows a responsible investment approach, which may cause it to be underweight in certain sectors (due to the avoidance criteria employed) and thus perform differently than funds that have a similar financial objective but which do not apply any avoidance criteria when selecting investments.
- The Fund may use derivatives with the aim of reducing risk or managing the portfolio more efficiently. However this introduces other risks, in particular, that a derivative counterparty may not meet its contractual obligations.
- If the Fund holds assets in currencies other than the base currency of the Fund, or you invest in a share/unit class of a different currency to the Fund (unless hedged, i.e. mitigated by taking an offsetting position in a related security), the value of your investment may be impacted by changes in exchange rates.
- Securities within the Fund could become hard to value or to sell at a desired time and price, especially in extreme market conditions when asset prices may be falling, increasing the risk of investment losses.
- The Fund may incur a higher level of transaction costs as a result of investing in less actively traded or less developed markets compared to a fund that invests in more active/developed markets.
- The Fund could lose money if a counterparty with which the Fund trades becomes unwilling or unable to meet its obligations, or as a result of failure or delay in operational processes or the failure of a third party provider.