AI: A long time coming and a long way to go
In the first installment of a three-part series, Portfolio Manager Denny Fish and Investment Strategist Michael McNurney explore how artificial intelligence (AI) has come to quickly dominate the investment landscape and what it means for the global economy and equity markets.

7 minute read
Key takeaways:
- The rapid adoption of AI is redefining how humans interact with technology, potentially leading to a boon in productivity not seen since the Industrial Revolution.
- The arrival of generative AI (GenAI) is made possible by the convergence of a series of powerful tech themes, including cloud computing, increased processing power, and an unprecedented amount of stored data available to analyze.
- Many industries are directly involved in AI’s deployment, among them semiconductor makers, internet-based AI platforms, and specialized software companies.
In the roughly 18 months since Open AI released ChatGPT, artificial intelligence (AI) has become an inescapable conversation topic within the investment community, corporate boardrooms, and policy circles. Given this attention, some may ask the question: Is AI really such a big deal? Our answer is a resounding “yes.”
The reasons are manifold. From the highest level, AI, in our view, forever changes how humans and businesses interact with technology. From a macro perspective, it has the potential to be the greatest productivity enhancer since the Industrial Revolution over 200 years ago. Lastly, with respect to the workplace and equities, we expect AI to provide an earnings tailwind as companies deploy it with the aim of streamlining costs, generating revenue and, in many instances, developing new products.
Artificial Intelligence has the potential to be the greatest productivity enhancer since the Industrial Revolution over 200 years ago.
On the shoulders of giants
ChatGPT’s arrival may have seemed like a lightning strike, but the concept of and predecessor technologies for AI were decades in the making. In fact, famed mathematician Alan Turing posed the question of whether computers could eventually think more than 70 years ago.
Over the decades, as processing power grew and algorithms became more sophisticated, computer applications could perform increasingly complex tasks that could indeed be viewed as steps toward thinking. However, programs such as IBM’s Big Blue – which famously defeated chess champion Gary Kasparov – were largely reacting to scenarios they had been programmed to navigate.
The advancements exemplified by ChatGPT are owed to large language models (LLM) and GenAI. These complementary technologies enable powerful algorithms to analyze massive data sets. LLM produces advanced predictive text, while GenAI can create original content based on its own inferences from data sources rather than take predefined cues from human inputs. Chatbots like ChatGPT, however, are just one example of the AI-enabled functionality that we expect to see deployed across the global economy in coming years.
Why AI now?
The parameters available to train AI platforms have grown exponentially, along with the capabilities of processors to analyze and make inferences from these massive data sets.
Number of parameters used by AI language models
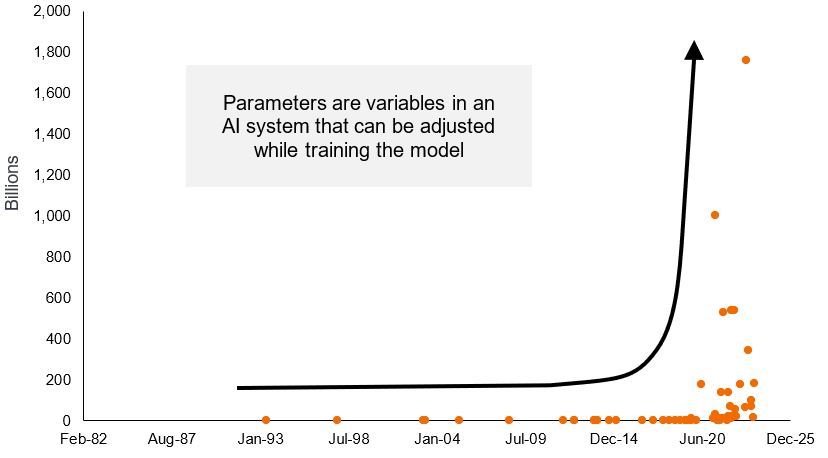
Source: Karl Rupp. “40 Years of Microprocessor Trend Data.”
That the promise of AI is only being delivered on now is no accident. It is due to the convergence of several essential inputs: First, an unprecedented amount of available data, thanks in part to the proliferation of the internet and the storage capabilities of the cloud. Second, the ability of cutting-edge graphic processing units (GPUs) and application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) to systematically absorb this data and maximize the information held within it. Third, advancements in memory chips. And fourth, increasingly sophisticated and specialized software applications that provide platforms upon which AI can be deployed.
Generative AI is the most recent step in this process, and while it has long been anticipated, a true understanding of its capabilities and use cases can only be gauged upon its arrival. This follows the pattern of earlier AI-related advancements, including analytical applications that could find patterns in large data sets, diagnose issues, and deliver predictive analytics.
Next up was machine learning, which could implement the lessons learned from these analytics. Even as we are only beginning to appreciate the power of GenAI, we recognize that the next stage of its evolution is artificial general intelligence (AGI) one day potentially being able to learn and reason on a human level.
Granted, the ability of AI algorithms to scour data, make connections, draw inferences and, when prompted, test hypotheses and come to conclusions, may not be the same as human thinking. But AI’s ability to rapidly leverage large data sets to achieve these objectives make it a powerful complement to workers in a vast array of professions and roles.
In this context, AI can be viewed as both its own secular theme and the culmination of other themes we’ve followed over the years, among them the cloud, the Internet of Things, and mobility. Their convergence, in our view, represents a generational shift in computer technology akin to the transition from mainframes to servers and personal computers and, more recently, the adoption of the internet and mobility.
The convergence of computing power and big data
Internet- and cloud-based big data, coupled with the advanced processing capabilities of GPUs and more sophisticated algorithms, are responsible for GenAI’s emergence.

Source: Janus Henderson Investors.
AI applications: An overview
Considering all the market buzz around AI, investors may be wondering whether they have missed the boat on gaining exposure to this theme. Hype often accompanies the emergence of a transformational technology, and with hype comes considerable noise. Still, we believe a unique feature of AI is the breadth of players across industries and value chains to which it can provide lasting benefits.
Perhaps the most fundamental AI benefactors are the facilitators – the companies that produce the GPUs and capital equipment required to create the physical infrastructure underpinning the AI ecosystem.
Next are the AI creators. These include the companies that have already released AI platforms, such as the major internet players and cloud service providers that have enormous data sets at their disposal. For some creators, AI will complement their own business models, and in others it can be viewed as a business unit servicing customers. Other creators include Software as a Service (SaaS) providers that use AI to reinforce their product offering and software companies focused on specific business verticals.
While these examples have AI imbedded in their DNA, the list of potential beneficiaries can be expanded to include companies across all industries that have the opportunity to leverage AI to drive positive business outcomes.
In addition to considering AI’s impacts on the corporate landscape –many of which have yet to be identified – investors concerned about being late to the AI party should recall the following maxim: The earnings potential of technological breakthroughs is typically overestimated in the near term while considerably underestimated over longer horizons.
This is likely the case with AI. While the innovators and early adopters have already been identified, investors – and often companies themselves – are still unsure of the full impact AI will have on various sectors, business models, and functions. One thing we believe, however, is that as with other innovative breakthroughs, there will be leaders and laggards, with the latter camp at risk of being disintermediated for failing to comprehend the magnitude of AI’s disruptive potential.
The progression
While investors are focused on early AI adopters, we believe the lion’s share of the technology’s commercial and investment ramifications have yet to play out.
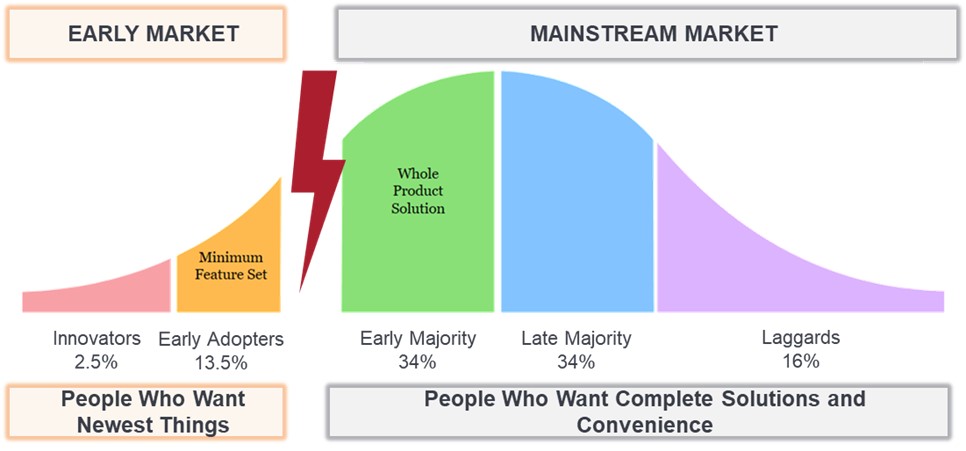
Source: Janus Henderson Investors.
The bigger picture
The context provided here centers on how AI may impact the corporate landscape. But to fully grasp the degree to which this revolutionary – as opposed to evolutionary – force could affect the global economy, consider what is already being hypothesized by analysts, economists, and policymakers.
By boosting productivity, many experts believe AI could influence economic growth, wages, the level of inflation, and even interest rates. Within financial markets, companies’ ability to effectively leverage AI will factor into their stock price, and AI’s aforementioned macro effects will be considerations for bond investors. The takeaway is that very few pockets of the global economy are immune to the rollout of AI.
In the next instalment, we will more closely examine AI applications in the workplace and the individual industries most likely to contribute to – and benefit from – the arrival of this major technological advancement.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Technology industries can be significantly affected by obsolescence of existing technology, short product cycles, falling prices and profits, competition from new market entrants, and general economic conditions. A concentrated investment in a single industry could be more volatile than the performance of less concentrated investments and the market as a whole.
All opinions and estimates in this information are subject to change without notice and are the views of the author at the time of publication. Janus Henderson is not under any obligation to update this information to the extent that it is or becomes out of date or incorrect. The information herein shall not in any way constitute advice or an invitation to invest. It is solely for information purposes and subject to change without notice. This information does not purport to be a comprehensive statement or description of any markets or securities referred to within. Any references to individual securities do not constitute a securities recommendation. Past performance is not indicative of future performance. The value of an investment and the income from it can fall as well as rise and you may not get back the amount originally invested.
Whilst Janus Henderson believe that the information is correct at the date of publication, no warranty or representation is given to this effect and no responsibility can be accepted by Janus Henderson to any end users for any action taken on the basis of this information.

